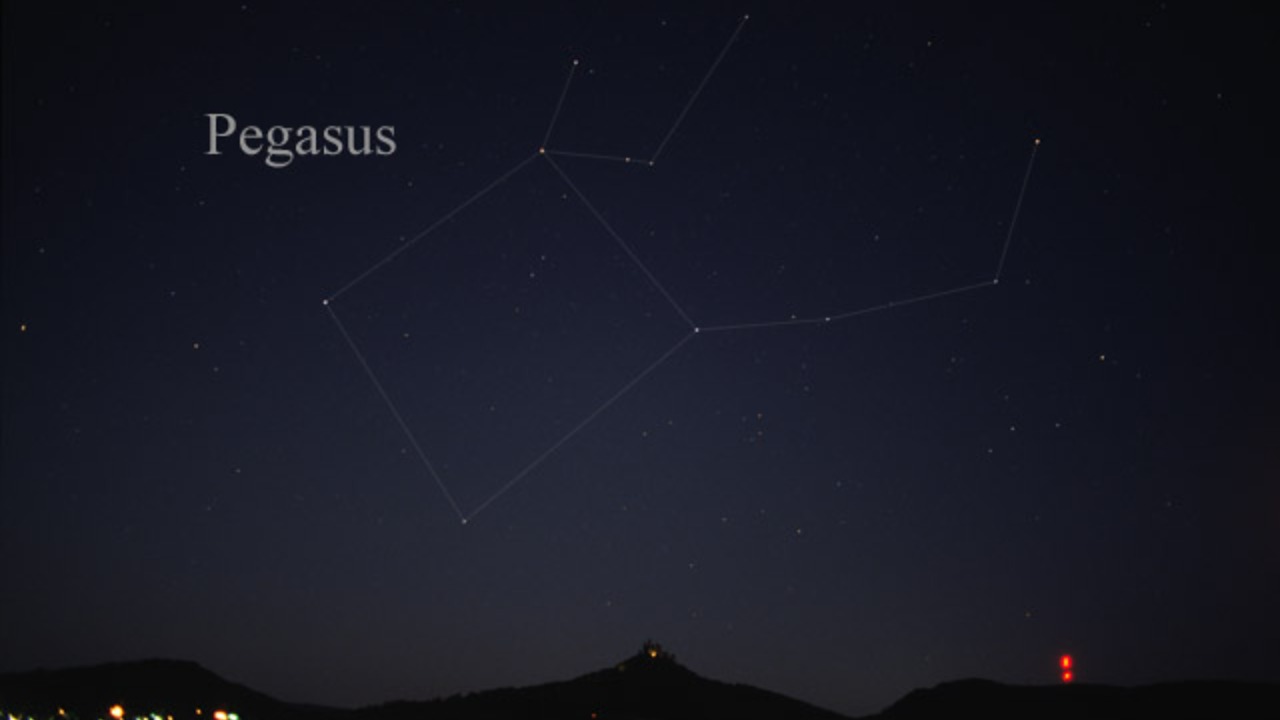
As autumn nights deepen in 2025, stargazers can witness the mythical winged horse Pegasus soaring across the sky, a constellation that’s become a highlight for observers since recent reports on November 16. This celestial figure, tied to ancient legends, offers a captivating view that’s easier to spot now compared to earlier in the year, drawing enthusiasts to clear skies for what experts call the best sky story ever unfolding overhead as of November 14 updates.
Origins of the Pegasus Legend
The constellation of Pegasus is steeped in rich Greek mythology, where it is said to have emerged from the blood of Medusa after the hero Perseus slayed her. This dramatic birth story has cemented Pegasus as a symbol of inspiration and flight in ancient tales. The mythological roots of Pegasus not only captivate those interested in the stories of old but also enhance the allure of the constellation for modern stargazers. The enduring appeal of Pegasus is evident in how it continues to inspire both storytellers and astronomers alike.
The shape of the Pegasus constellation mimics that of a flying horse, with key stars forming its body. This configuration has been highlighted in timeless sky narratives, making it a favorite among those who enjoy tracing the outlines of mythological figures in the night sky. The constellation’s distinctive shape is formed by several bright stars, which together create an image that has fascinated observers for centuries. This connection between ancient myth and modern astronomy underscores the timeless nature of human curiosity about the cosmos.
In modern astronomy, Pegasus holds a prominent place in autumn viewing guides. Its visibility during this season makes it a focal point for both amateur and professional astronomers. The constellation’s position in the sky during the fall months allows for optimal viewing conditions, drawing enthusiasts to observe its majestic form. This seasonal prominence ensures that Pegasus remains a staple in the repertoire of celestial wonders that capture the imagination of those who gaze upwards.
Identifying Pegasus in the Night Sky
One of the easiest ways to identify Pegasus in the night sky is by locating the Great Square of Pegasus, a box-like asterism that outlines the horse’s body. This prominent feature is visible high overhead post-sunset, making it an accessible entry point for those new to stargazing. The Great Square serves as a guide to tracing the rest of the constellation, allowing observers to appreciate the full extent of Pegasus’s form against the backdrop of the autumn sky.
To further trace the winged form of Pegasus, stargazers can look for Enif, the bright star that marks the nose of the horse. Other key markers include Scheat and Markab, which help to define the constellation’s shape. These stars are part of the larger pattern that makes up Pegasus, and their brightness aids in distinguishing the constellation from surrounding celestial features. For those seeking a clearer view of fainter details, tools like binoculars can enhance the experience, building on recent stargazing tips for seasonal observation.
Identifying Pegasus is not only a rewarding challenge for amateur astronomers but also an opportunity to engage with the broader narrative of the night sky. By learning to recognize this constellation, observers can deepen their understanding of celestial patterns and the stories they tell. This engagement with the night sky fosters a sense of connection to both the natural world and the rich tapestry of human history that has been woven into the stars.
Optimal Viewing Times This Autumn
Mid-to-late November 2025 marks the peak visibility for Pegasus, when the constellation rises earlier in the evening compared to October’s lower horizon position. This timing allows for extended viewing opportunities, as Pegasus can be seen prominently in the sky during the early evening hours. The shift in visibility from October to November highlights the dynamic nature of the night sky and the importance of timing in astronomical observation.
Regional variations also play a role in the visibility of Pegasus, with clearer sights available from northern latitudes where the constellation culminates around midnight. These variations mean that observers in different locations may experience Pegasus differently, adding a layer of complexity to the stargazing experience. Understanding these regional differences can enhance the appreciation of the constellation and its place in the broader celestial landscape.
Light pollution is a significant factor that can impact the viewing experience, making dark-sky sites ideal for observing Pegasus. These locations offer the best conditions for stargazing, allowing the constellation to be seen in all its glory. As the nights grow shorter, finding a suitable viewing spot becomes increasingly important for those wishing to capture the full beauty of Pegasus. This emphasis on optimal conditions underscores the importance of preserving dark skies for future generations of astronomers.
Pegasus and Companion Celestial Events
Pegasus is not alone in the night sky; it neighbors other notable celestial features such as Andromeda and the Pleiades, creating a rich autumn tableau. This proximity offers a unique opportunity for stargazers to explore multiple constellations and star clusters in a single evening. The waning moon phases post-full further enhance the visibility of these features, making this period particularly favorable for celestial observation.
As the seasons shift, so too does the position of Pegasus in the sky. In December, the constellation arcs higher compared to its current November trajectory, signaling evolving sky patterns. These changes provide a dynamic backdrop for stargazing, as observers can witness the gradual transformation of the night sky over time. This seasonal movement of Pegasus serves as a reminder of the ever-changing nature of the cosmos and the ongoing cycle of celestial events.
For those interested in capturing the beauty of Pegasus, photography and sketching offer creative ways to document the constellation. These activities allow amateur astronomers to engage with the night sky in a personal and meaningful way, contributing to the broader storytelling of the skies. By sharing their observations, stargazers can connect with others who share their passion for the stars, fostering a sense of community and shared exploration that inspires deeper curiosity and appreciation for our vast cosmic surroundings.